Search engines, technology and list
They are no longer just a mean to find a site on a topic, but they want to go beyond, to answer questions for example, and became for webmasters the essential part of the environment.
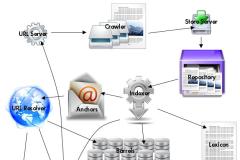
Technology of search engines
For years, the technique was to attach a set of keywords to a page, and display in the results pages links corresponding to the keywords of the user query.
To improve the relevance, Google invented PageRank: pages are ranked by the number and quality of links pointing to them, for a group of keywords.
Besides PageRank, we see the BrowseRank which ranks pages based on user activity, TrustRank for the confidence of the source. The FreshRank aims to evaluate the freshness of the contents and pertinence in the news.
SEOs strive to understand the workings of the algorithm, but it is futile to try to assign it a logic. At least from the perspective of the webmaster, because the engine has its own logic. A website is from the view point of the engine like a star lost in an infinite number of galaxies. Just a small point of light. The webmaster does not always understand how the engine ranks its site, but for the latter it comes to direct users in this star cluster and this optimally. We often underestimate the constrain means that are implied by the word optimally.

Knowledge base of objects
Bing tries to move from text to the object, just like Google. In 2012, 300 million object have a card in the database of Microsoft. When a request is made, the engine attempts to identify the relevant object and returns the results in relation to this object. All information collected on the Web, on the pages or on social sites, are associated with an object. This provides information on it when it is identified in the request.
Google has a similar tool that begins to take shape in the SERPs in 2012, and that it calls Knowledge Graph. This is to display in the results page next to the link list, information about the object of research: people, places, works etc. ... This in text and image.
Data come from Freebase, Wikipedia, CIA World Factbook and other sources. It contains in 2012 500 million objects and 3.5 billion of facts about these objects. As an example, if the query is identified as Marie Curie, the page displays a photo of her, a biography, pictures of people in connection with her. If it is a painter, there will be images of his most famous paintings.
Video of Knowledge Graph.
This type of result page is the subject of an experiment by Google on www.wydl.com since 2011 and it was expected that it passes to the main search engine, which now began to in 2012.
List of search engines
You can register for free and add your site on search engines listed below, the most notables are in the list.
- Ask.com
- Bing
Replaces Microsoft Live Search and is intended as a decision engine. Research is done by category. - DuckDuckGo
A different view on the Web. No private data used.
By typing !sp + keywords, you may access Google's index without using their interface. - Entireweb.com
- Google
The most popular. - Lycos.com
- Perplexity.ai
Search engine using A.I. like Chat GPT to answer questions. - Virgilio.it
Italian. - Wolfram Alpha.
Engine knowledge to answer scientific questions. - You.com
Provides an A.I-based response, it claims. With links on websites. Based on Google results but with more user tracking. If you fear being spied on, this is not the best tool.
Resources
- CommonCrawl. This non-profit foundation provides an index of 5 billion of links on Web pages. Enough to create its own search engine!
- IndexTank. The search engine of LinkedIn is open sourced. This includes a framework to maintain the index.
- DuckDuckGo source code. The search engine that is growing is open sourced too on GitHub.