The Panda patent made simple
Simplified description of the patent 8,682,892 for ranking pages, images and other resources, assumed penalizing poor quality sites, mainly content farms.
Three years later is revealed the Panda algorithm which has demoted tens of million of websites (about 20% of 300 million), questioned the job of webmaster and bankrupted countless ecommerce websites. We will be delighted to discover that the famous algorithm that is supposed to judge the quality of websites and "create a healthy ecosystem" in the words of Google, is is a simple equation: M = IL / RQ!
There is not doubt, however, the study of patent 8,682,892 describes a method for ranking whose effects perfectly match the new behavior of the search engine launched February 24, 2011 ...
- This has benefited the big sites like Amazon, eBay, which saw an increase of 30 % of their traffic.
- This has affected mainly medium-sized sites. Numerous ecommerce sites have closed their doors.
- And benefited brand sites.
- Sites are affected in their entirety and not just pages of lesser interest .
- Older sites are more affected than new ones.
- The sites affected have almost never recovered their traffic, even when they changed their content to improve it. Some, however, were able to recover by removing a large part of their pages.
- 12 % of sites have been affected by the first iteration, and even more with the next ones.
- We know that Panda requires enormous resources and was applied first by an independent program that was ran almost every month. We now know that it is to build scores of resource groups of all sites of the Web.
- This was introduced by Google as a way to downgrade pages of lesser quality. This is the goal given in the patent.
Google then considered that this method deserves a patent and the specification 8,682,892 was filed on September 28, 2012.
And here in detail this method ...
The Panda method
The process used to modify the rankings according to the r Panda factor is to partition the index into groups of resources considered related.
1) Groups of resources are defined
The entire Web is partitioned into groups of resource. Resources are pages, images and other documents that may be in the result and are in the index.
Resources are added to the same group based on the URLs, and the group includes all documents of a domain, sub-domain, a set of domains, or even the same hosting.
Google may also infer the group membership on the basis of common elements : the same presentation, same style sheet ... (hopefully it does not equate to a group all sites that use Bootstrap !) .
The group (website or collection of sites) being defined, it is given a Panda factor that will be applied to each page of the group. We will see later how this factor is calculated.
To simplify the description, we designate a group of resource by "site" and a resource by "page", but you remember that it's more complicated than that.
2 ) The initial score of a page is defined.
When the system receives a request from a user, it also receives a list of pages each with an initial score for ranking.
It is previously calculated by the standard algorithm according to 200 criteria, including PageRank.
It will by modified by the Panda factor.
3) The group is identified...
For each page, the program identifies the site to which it belongs on the basis of the URL. Knowing the site, it gets the Panda factor associated.
4 ) A factor specific to the page is generated
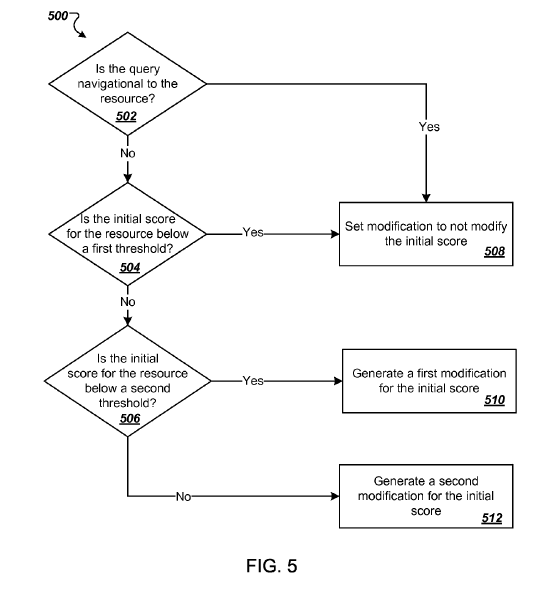
From the Panda site factor is calculated something more specific. To do so, the initial score of the page is compared to two successive tresholds.
If the initial score is below a first treshold, the Panda factor is canceled.
If the initial score is between the first treshold and a second higher treshold, a specific factor is calculated which decreases when the original score increases.
If the initial score is above the second treshold, the Panda group factor is modified by a formula or algorithm, that softens the effect.
5) Navigational queries are excluded
When the user makes a query which aims to find a site or a particular page, giving the domain or characteristics related to the site or page, the Panda factor is ignored and the page will be ranked according to its initial score.
6 ) The modification factor is applied to the initial score
Panda factor is multiplied to the initial score for a new ranking score, and it will be used to show the results.
Calculation of the modification factor
Here is how is set the Panda factor for a group of resource, ie a site or a set of related sites.
1) The index is partitioned into groups of resource
This is based on the URL, but also on other factors to identify the same owner for a set of resources. A group is defined as a domain or sub-domain or set of domains belonging to the same person or organization.
2) The number of independent links to pages for each site is counted
Explicit links pointing to the site are considered, but also references to this site as the domain even without link tag. The links are independent if they do not belong to the same group of resources, so depending on the circumstances the same domain, subdomain, or sites with a same owner or interrelated.
But the system can also try to find a relationship between the source page and the target page. The same style sheet, similar content, the same images. A score of independence may be calculated and if this value is too low it is concluded that the link is not independent.
The system retains only a link to each page of the source site.
The count of independent links is stored.
3) The number of requests to the pages of the site is counted
The system counts the number of reference queries to each site. These are queries made by different users to the pages of the site. Users are identified by IP address, cookies or any other means.
The count of reference requests is stored.
4) A ratio is defined to get the Panda factor
Modification factor = number of independent links / number of reference queries.
5) The Panda factor is normalized
In some implementation the modification factor is normalized.
The number of intervals reference queries is defined and the index is partitioned into a plurality of sites belonging to the same interval.
The Panda factor of each site is normalized on the basis of other sites in the same partition, so the same interval.
To do this is calculated the mean or median or other measure of this kind and this formula is applied:
Normalized modification factor = modification factor - measure / measure.
The new value is stored in place of the modification factor of the group.
Further modifications
Panda has received several modifications, some of which were made public...
Niches. Some sites provide a unique information in specific fields and are provided very few incoming links. Panda was corrected to save these sites.
Matt Cutts also said that in a new iteration, Panda took into account the fact that when registered users on Google exclude a site from results pages, it then gets a reduced score.
On 20 May 2014, a major update allowed many small sites out of the Panda sandbox. Although the nature of the modification of the algorithm has not been disclosed, it is clear that Google finally realized that a small site can not have as many links back a big site. Therefore responded to the criticism in conclusion.
The algorithm and its effects
Favoring backlinks, Panda promotes new pages and news, the buzz. While backlinks accumulated by older sites disappear with time...
Panda does not remove nonsense from results pages, such as "if you want a screw that does not break, buy a more solid." But that kind of answer is now provided by large general sites that take the place of content farms. A new trend?
SEO loses much of its interest with Panda. No SEO work can increase the number of completely independent backlinks. They depend on the content. And activism. But knowledge of search engines remains useful for solving many problems of the webmaster, like redirects, domain change, duplicate, microdata, etc...
A equal quality, the higher a website has visitors, the greater are the chances of getting backlinks. The ratio explains why a site may not recover after being penalized by Panda: how to get more backlinks while the traffic has been significantly reduced ?
Knowing that a site gets 10,000 visitors per day, and another only 1000. If each of the two published a page on the same topic with the same keywords and get the same initial score, the first will get ten times backlinks thanks to the number of visitors and thus a Panda factor ten times better.
But how this indicates a better quality of content?
When the answer to a complex question is not on a large site, it becomes more difficult to find. The popularity is favored.
According to the ratio used, if a site has an image that becomes viral and gets a million references, all that will be published on this site will be considered of quality and get a better ranking. The quality of the sites, according to a notion that Google has, is estimated by an algorithm of poor quality.
Update May 2014: In the new iteration of May 20, it seems that have been taken into account (after 3 years) the fact that a smaller site can not get as many backlinks even with original and informative content..
Author: Denis Sureau, April 14 2014.
More figures belonging to the patent:
- Schema of a search system. On which operate the patented method.
- Steps of the Panda algorithm.
- Calculation of the modification factor.
- Normalisation of the modification factor.