What we should know about the PageRank
Google's PageRank is a part of an algorithm and a value to measure the popularity and the relevance of a page on the Web. It is a leading indicator of ranking in search results.
A legend spread by webmasters who have a very partial understanding of how search engine work argues that "PageRank is dead."
This is not the case and it will never be the case. While innovative search engines like Wolfram Alpha have a completely different back-end, however they represent a tiny fraction of web searches, and they provide content pages they produce, not lists of external pages and they did not deal with spam. PageRank is still needed to assess the value of a page.
 The name PageRank is a registered trademark.
The name PageRank is a registered trademark.
It was originally a pun on the word page and the name of one of the two Google founders, Larry Page.- The success of Google was born out of the use of the PageRank algorithm.
By which ranks sites according to links and not on the number of keywords in the page as did the search engine AltaVista (few Internet still know AltaVista). - The PageRank contributes to the ranking of a page in Google results.
But it is a signal among many others.
See the Google patent for scoring Web pages. - PageRank is an index reflecting the proportion in number and importance of links on a page.
It does not depends only on the number of back links: The PR of pages is the most important factor.
(Ref: The Anatomy of a Large-Scale Hypertextual Web Search Engine). - The pages are crawled in order of PageRank.
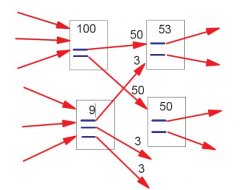
The pages that have the highest PR are scanned more often and more completely. Linked pages will be too, but the most we follow links and the the most keeping track fades. - The PR of a page sent to the linked pages is divided by the number of links.
The value passed corresponds to the PR of the page divided by the number of links on the page, as shown in the graph on the right., whether they are in follow or nofollow.
(Ref: The Anatomy of a Large-Scale Hypertextual Web Search Engine). - The nofollow attribute in a link does not pass the PR to the page that is linked.
But its share of undistributed PR is not redistributed to other links, it is lost.
See PageRank and nofollow. - The increase in PageRank score has a progressive difficulty.
It does not depend linearly on the importance of backlinks but logarithmically. So when we progress continuously, it takes much more time to go from 4 to 5 than from 3 to 4. - Several links in a page have no more value than one.
A page with several links to another same page does not transmit more PR than with one. Only the first is taken into account, in addition, if the anchors differ, it is the anchor of the first link that is taken into account to assign keywords to the target. - All pages are equal.
The algorithm does not distinguish the index page or pages at the root of the site and deep pages. He distinguishes "Landing pages", those that are popular and have the most backlinks and others. Popular pages transmit PR and traffic to others. Internal links should be studied according to this. - PageRank is transmitted through a link to an image.
It is official from Google with no more details. - A 301 redirect means losing some PageRank
When a page is redirected by a 301 HTTP code, the new page does not keep the full PageRank, it is dininushed by a small factor. As a result, the new page could lose its ranking. This was confirmed by Matt Cutts (an has been verified in live). - Changing the content of a page can suppress the weight of backlinks
The links refer to a specific content. If the page changes, it should have new links to retain its PR. Changing the content of a page once it became popular is a technique of spammers, so it can trigg a penalty in addition to a loss of PR. - A site with a better PR can be ranked below other sites
Because the page of results is related to a group of keywords, while the PageRank reflects the number and quality of backlinks to the page regardless of the query. It is possible that another page is best ranked on a group of different keywords. - Google considers that the page with the higher PageRank is the original, even if newer!
When two pages are identical, and if the date of indexing is not sufficient to know what is the original and what is the copy, This was clearly stated in an interview of Matt Cuts by Stephan Spencer and confirmed by a post on the Google's blog about duplicate content. - Google tried an algorithm that ignores backlinks
Matt Cutts explained in a video that they tried that and the results are much worse in terms of relevance than the algorithm that takes tehm into account and then the experience did not go out of the lab. - There are enterprises which claim to provide 10 points PR
But according to Google, nobody can garantee a PageRank, for any position. (And I know only a dozen of big websites with a 10 PR). - In 2016, Google stopped to make PageRank value publicly available. It was not updated since 2014. The indicator had already disappeared from Google Webmaster tools in 2009.
References: SEO for bloggers, bBy Matt Cutts, The Anatomy of a Large-Scale Hypertextual Web Search Engine by Google founders.