MySQL or MariaDB?)
The most popular relational database manager is installed on million servers.
This includes Youtube, Flickr, Yahoo!, Facebook (beside Hadoop), Twitter.
MySQL is used for very large sites or small databases.
The Tumblr site supports 60 billion rows on MySQL which requires 200 dedicated servers and a special tool, Jetpants but you may use it for a single table and tow columns.

MySQL was created in 1995 by David Axmark, Allan Larsson and Michael Widenius who founded the company MySQL AB to market it.
In June 2000 it passed under the GPL but it remains dual-licensed and it is possible to purchase a proprietary license especially to integrate it in other software whose license is not compatible with GPL.
The company was acquired by Sun on February 26 2008. When it was itself acquired by Oracle on 20 April 2009, MySQL got a new owner (and users concerned, see below).
MySQL's popularity is declining since 2012 as the software tends to be replaced by MariaDB (from the same author), more efficient and with more responsive maintainers.
The creator gave the software the name of his second daughter, Maria, while MySQL comes form My that is that of the first (this is the source of a confusion, so many products have wanted to emulate MySQL by using the My prefix, to mean "mine").
In May 2017, the European Commission released € 25 million for the development and promotion of MariaDB. This will allow it to expand his team and accelerate its development.
A design oriented to reading
MySQL is optimized for reading, it is well suited for the Web where viewing pages is more frequent than their creation or update.
It supports concurrent requests for multiple users (unlike for example, SQLite which can process only one at a time).
It is compatible with SQL2 and the procedural language PL/SQL since version 5.
MySQL is often used in conjunction with MemCached, a program that maintains the database in memory to speed up transactions. Large sites like Facebook, Twitter do use it. It is available for Wordpress, Joomla, Drupal.
Lot of storage engines may be used by the system whose purpose is to manage the creating and deleting of data in the base, and the corresponding storage in the file system:
- MyISAM. The initial default engine.
- InnoDB. More powerful, bought by Oracle in October 2005, became the default engine starting with version 5.5.
- BerkeleyDB. Was bought by Oracle in February 2006, obsolete since MySQL 5.1.
- And many others.
MySQL Cluster is a multi-server version. It distributes the load and can operate in real time without waiting or failure. In this case the NDB engine is used beside one of more traditional engine above. Version 7.2GA can process one billion transactions per minute. It is open source, only the support requires a fee.
You should know, however, that if MySQL Cluster is provided by Oracle for free (on their servers), it is no longer when traffic becomes too great and Oracle offers a priced solution instead.
Most programming languages can be used to access the DBMS, so to make requests. The most commonly used languages are PHP and Java.
The M first letter MySQL gives a letter to LAMP (Linux Apache MySQL PHP), a popular server system of websites.
MySQL or MariaDB?
After the acquisition of Sun by Oracle, a database company that has in MySQL, which is a free product, a competitor to its paid products, how can be the future of MySQL? That of Delphi?
Oracle is trying to monetize the software to replace its main product, Oracle Database, with additions that cost between 2000 and 10000 dollars per computer.
The creator of MySQL, Michael Widenius, has his opinion: To be free ot not to be free. He want to create a "Fedora" for MySQL, an independent project free of any commercial attaches.
As MySQL is becoming more and more commercial, alternatives will eventually replace it. At $2000 per server per year, this may become inevitable. Oracle seems to inadvertently encourage this trend by performing a first step: the tests that check the operation of the software are no longer provided.
MariaDB tends to take the place of MySQL. By one of creators of MySQL, Michael Widenius, it is derived from MySQL 5.1 but is faster. Use InnoDB or XtraDB and adds features that Oracle provides only on the commercial version of MySQL.
In addition, this distribution grows even with time. Version 10 allows for example to view data in a Cassandra database or through ODBC.
Wikipedia migrated from MySQL to MariaDB in 2013 and Linux distros do the same (Fedora in the 19 version, Suze in 12.3, Slackware in 14.1, Arch Linux in 2013.03), Red Hat in 7. Google uses (on thousand of servers) MariaDB and even contributes in its development.
See the list of differences between MariaDB and MySQL. Not there are even more differences with each new version.
And despite the differences, you can directly install MariaDB to replace MySQL, without change in the bases. Under Linux, with just one command.
However MySQL continues to evolve and the 5.7.7 release implements the storage of JSON objects in a binary format for quick access. MySQL is not yet buried.
Market shares
In May 2015. These figures (number of posts) are given by the DB-Engine site and are based on many criteria: references on the media, jobs offers, searches in engines ....
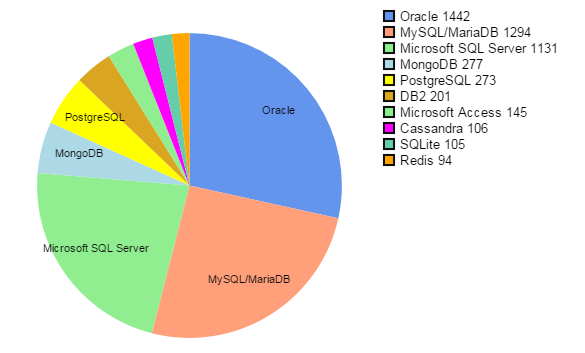
Chart by Scriptol.com
Oracle and Microsoft SQL Server are down sharply compared to May 2014. MySQL slightly down. Other are growing. Start-ups choose often Postgre.
Alternatives to MySQL
Besides MariaDB , some other forks were created that try to maintain compatibility:
- Drizzle. MySQL lightweiht for the cloud. Derived from MySQL 6.0 that was in development.
- Percona Server. Uses the XtraDB storage engine.
- WebScaleSQL is a open source joint project of Facebook, Google, Twitter and others to a version of MySQL which can support large databases and a large number of connections. Of course, Oracle is not part of the contributors, although the owner of MySQL.
PostgreSQL is also seen as a open source alternative. But the software is not exactly in the same category, it is more difficult to install and designed especially for large databases, where writing is as common as reading. It is rather an alternative to Oracle.
Uber migrated from PostgreSQL to MySQL (the Percona fork) plus the Schemaless layer, but this depends of their service as Schemaless turns the database into NoSQL. They see a speed up in frequent updates of rows. To be clear, Uber migrated from MySQL to PostgreSQL in 2013, and then once introduced Schemaless, returned to MySQL.
Moreover, MemSQL, wants to be the DBMS of tomorrow. It runs entirely in memory, accessing the disk at intervals to save the data to be retained and thus is 30 times faster than MySQL. Actually, MySQL database can also be loaded in memory, the difference being in how the data is periodically saved to disk.
But these figures are disputed by arguing that the benchmarks are done on the default configuration and that we can configure MySQL to make it faster and also durability is disabled to reach the speed. Two other programs work the same way, Hana from SAP and VoltDB.
And there are also NoSQL, a set of other designs : key-values couples, graphs, documents... NoSQL is often seen as a solution for companies whose databases become huge, however companies like Yahoo! and Twitter have shown that MySQL in clusters (in custom version) is able to support very large databases. Moreover you can associate softwares to MySQL to manage different structures, see The databases of Web enterprises.
Downloads
- MySQL. Download a version of the software.
- phpMyAdmin. Interface to manage online a database. This may be done also from LibreOffice,
- HeidiSQL. Work locally and can manage a remote database. (Windows).