.NET, an alternative to Java
The .NET framework (pronounced Dotnet) is a runtime environment for software, created by Microsoft. It runs on Windows and there is a compatible software for Linux. .NET offers a library of functions for graphical interfaces, data access, networks and Web applications, plus compilers and a virtual machine. It allows users to run applications on the classic desktop next to Modern UI applications that have WinRT for backend.
On 12 November 2014, the company announced that it made open source .NET (under MIT license) and it now also work on Linux and MacOS.
.NET then designates three different products that all work with the C# language:
- .NET Framework, the origin, which runs on Windows only.
- .NET Core, the multi-platform version, under development but which may already be suitable for server-side applications.
- Mono, a desktop or Android or iOS mobile version that gradually shares .NET Core code.
With the introduction of .NET 5 in 2019, there is only one platform running on Windows, Linux, Mac, Android and iOS. It replaces .NET Framework on Windows, .NET Core, and Mono on other systems.

The programmer is primarily concerned with the choice of a programming language and tools to compile and APIs available to build the application. The following languages work on .NET: Ada, Basic, C#, C++, COBOL, Eiffel, Fortran, Haskell, Oberon, Pascal, Perl, Python, Ruby, Scheme , SmallTalk. See the full list.
Move to open source and .NET Core
In April 2014, Microsoft decided to make .NET really open source and to put it under the auspices of an independent foundation, the .NET Foundation. It provides now the source code of C# and Visual Basic compilers for different systems, by taking the code from Microsoft and from Mono. ASP.NET is also open source. For robotics, the Micro Framework will also be managed by the foundation and is under the Apache license.
In November 2014 Microsoft brings itself .NET on Linux and Mac OS. This is comprised of the core runtime and framework, in addition to ASP.NET and the C# compiler. The runtime, ie the JIT will be provided on GitHub in 2015.
Even Visual Studio becomes free in the community edition.
Why this move to open source? Making .NET more open will have many benefits:
- The development of their Azure platform, which support Linux, a source of considerable revenue to come: all the great actors of the Web launched their own version of cloud computing.
- Compatibility between systems can promote Microsoft's products such as server, database, and more.
- Attracting more developers on Windows Phone.
In 2015, Microsoft introduces .NET core, a new modular architecture to replace the .NET framework (which was actually several frameworks for different types of systems). It provides a single base class library to any devices and is open source. It allows to implement ASP.NET on Linux for example.
In 2018, Microsoft announces the support of Windows Form, WPF and UWP XAML in .Net Core 3. This makes .Net Core the successor of .Net Framework with the advantage that one does not have to install different versions of the framework depending on the application as it was the case.
But this only concerns Windows: Windows Form depends on Windows and can not be fully ported to Linux or Mac. Windows Forms depends on GDI Plus and WPF on DirectX, two Windows-specific graphics libraries. It is planned to make them open source, however.
In May 2019 Microsoft announces the end of the .NET Framework that will remain in version 4, and which is replaced by .NET 5, a single and universal version that replaces also .NET Core, Mono, Xamarin. It will be able to produce WebAssembly code too.
What is open source in .NET?
In the diagram below (from Microsoft, grayed by Scriptol.com), open source components are on a colored background and on a gray background closed components, which work only on Windows.
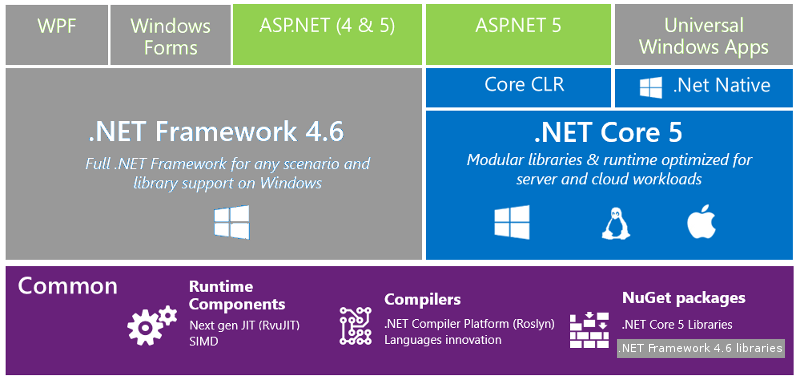
Open source:
- The Roslyn compilation platform for C# and Visual Basic with all the tools. Languages are compiled into IL code running on any desktop and mobile OS.
- The new generation of JIT RyuJIT interprets the IL code and converts it into native code. This in the first run, then the native code is executed directly. It works on the desktop and the server, but with 64-bit processors only.
It supports the SIMD protocol for parallel execution on multiple data. - .NET Core is a modular framework running on all platforms. This is a set of classes providing all necessary functions to applications.
It's portable and a open source alternative to the framework 4.6 and earlier versions for Windows. - Core CLR. Runtime of .NET applications, in binary.
- .NET Native. AOT compiler that translates C# or any other language to native. The application is faster and more compact than with the JIT. Microsoft claims a speed up of of 40% beside the advantage of eliminating dependence to the runtime.
- ASP.NET. Framework for Web applications running on the server side. Alternative to PHP, Node, Rail, etc ...
- WCF (Windows Communication Fundation). Put on Github on May 20, 2015. It is a web service framework, a REST platform (among others).
Closed:
- .NET Framework. It is provided on every recent version of Windows for modern apps.
- The libraries of the framework.
- WPF. Present since Windows Vista for GUI.
- Windows Forms. Graphical components.
- Universal Windows App. Application model for the Windows Store (for mobile shop and "modern UI applications" on Windows), which works with .NET Native, and therefore compiled into binary code.
Source code of .NET on GitHub.
A standard API
In September 2016, Microsoft announced the creation of a standard API for all .NET platforms: .NET Framework designed from the outset for Windows, .NET Core, the open source and portable version, and Mono, Xamarin version (now owned by Microsoft) for mobile OS other than Windows.
This corresponds to the following diagram:
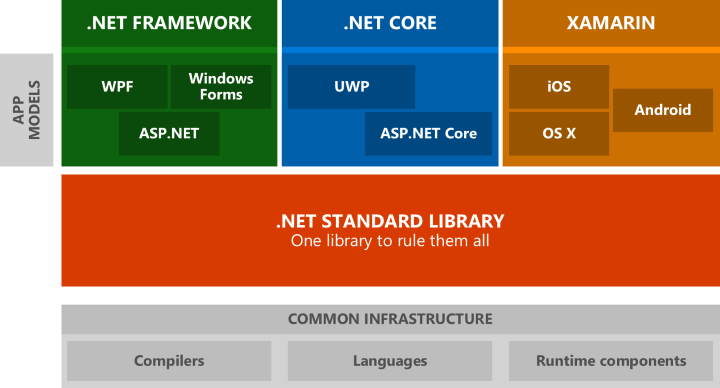
The .NET Framework developers will not need to change their code: WPF interfaces or else remain the same. The new API allows especially to extend the possibilities of .NET Core.
Java vs. .NET? Which platform to choose?
To build an application now should we choose Java or. NET? Compatibility and richness of functionalities are the keys to a better choice, but other factor must be taken into account.
Since November 2008, Java is under a open source license, GPL, partially (the mobile version is not).
Many programming languages have been ported on this platform and are compiled to bytecode interpreted by the JVM. This includes Python and Ruby.
.NET is now managed by an independent foundation, and since November 2014 is now as free as Java (which is not free on mobiles in fact). We also have a free version of Visual Studio to make apps for any systems.
C# is more modern and more complete than Java but no more than Scala + the Java library. We will choose mainly on what provides each library for a given application. The advantage of Java is that older applications work with every new runtime, while .NET applications require a specific version of the runtime: you may have to install several older versions on your computer...
XAML or JavaFX
Mono and .NET had another advantage that was Silverlight, a Web technology using a lighweight multi-browsers version of .NET, and Mono provided a Linux port, Moonlight (which is now dropped).
But Silverlight is not supported in the Modern UI interface under Windows 8 and replaced by HTML 5 + JavaScript or XAML + C#. Whether XAML or HTML 5, even if the principles differ, it is easy to describe an interface with a declarative language.
For its part, Java includes JavaFX, that the main development tools (see at bottom) support.
We can say that both platforms have a tool for creating effective graphical user interface and that enhances productivity.
Publishers are more than reluctant to use the Modern UI to the extent that a game publisher has launched its own version of Linux, SteamOS to avoid it, and manufacturers are considering replacing MUI by Android operating under Windows! This second initiative is in favor of Java.
Mono and .NET Core
Mono is a version of .NET compatible with Linux, made by Novell. After the acquisition by Attachmate of Novell, the Mono development team has decided to form an independent company, Xamarin. They continue the Mono project and provides commercial version for smartphones, including Android and IOS.
Mono is portable: it can run on any UNIX, MacOS and Windows. An advantage of Mono is that it is possible to compile C# into native code for all theses systems, from the exact same source code, and even building games as shown by Unity, which is specialized in games for Mono. They also work on mobile phones and game consoles.
.NET Core was the new version of the plateform launched by Microsoft to make .NET portable, especially for use on Linux server in its Azure cloud serice. It competes with Mono, but does not offer the same features yet in 2018. Producing an executable still requires Mono.
These frameworks use the same Roslyn compiler.
Both Mono and .NET Core are now replaced by a single framework, .NET 5.
Mobiles
Even if you program on the desktop, mobiles are a factor to consider because it is a plus if you can reuse your experience a day on these devices. It is also an area where future development will be the most important.
The Java virtual machine, not free on smartphones, is supplanted by Dalvik, an alternative virtual machine for Android which is ported to some other OS too.
It is possible to program in C# on Android thanks to the port of .NET by Xamarin. It is the language of choice on Windows Phone.
Given the importance of Android, Java is the language that prevails on smartphones. The true alternative is here with Objective C for iOS.
In 2014, Microsoft added to Visual Studio .NET Native. It provides the option to compile the source code into binary language for the Windows Store, so mobile or Windows 8. Then we skip the step to compile the bytecode at the first use of an application. This saves the space occupied by files in intermediate language.
Conclusion
Java comes with the advantages of seniority: stability, community, documentation, many development tools while .NET offers more openness: almost all languages, new ideas.
Under Windows, .NET is kept for desktop applications, but is replaced by a subset for immersive applications on Modern UI. And MUI is the preferred interface for future Windows applications. So if you looking for a universal portability, HTML 5 may in fact be the solution.
If you choose .NET, download the Visual Studio IDE to build .applications.
And if you are unsure, know that JSC recompiles .NET assemblies to JavaScript, PHP or Java.
Tools
LLILC. LLVM based compiler for MSIL code. Alternative to JIT and AOT compiler.