Differences Between Drupal and Wordpress
Webmasters who started a site on Wordpress, because it's easy to install and use, may be tempted to move to a CMS with a universal vocation and offering wider opportunities as Drupal.
You can do almost all kinds of sites with Wordpress (blog, ecommerce, digg-like), but with Drupal too with wider abilities.
You should know that changing from one to another is like moving from one world to another, very different.
The two programs have much in common:
* Free and open source.
* Multi-users with several levels of permissions.
* Support an API blog.
* Templates.
* Comments on articles.
* Significant permalinks.
* Generating RSS feeds.
* Multi-languages.
* Modules (plugins for Wordpress).
What we will study are the differences ...
The code
Wordpress is directly based on MySQL while Drupal has a common interface to databases, and can use PostgreSQL too.
Wordpress has its own template system. Its tags must be used to make custom designs. While Drupal allows the use of different languages templates: Smarty, PHPTAL. The default template engine is PHPTemplate.
The page structure
Drupal offers much flexibility to the composition of a template. Its blocks can be positioned anywhere on the page while Wordpress' widgets must be placed into specific areas (the sidebars).
Types of content
There are several predefined categories of content under Wordpress: posts and pages, comments...
Drupal offers a single basic structure, the node, from which we can build any type of editorial container. Three predefined types are provided: book, page and story.
A new type of content is defined by adding extra fields (as we add variables to an inherited class, for programmers).
On Wordpress we can create customized fields that serves the same purpose but is less sophisticated.
Editing
Wordpress incorporates an improved version of the Tiny MCE online editor. While Drupal leaves the choice of the editor, so you must install Tiny MCE or another editor to have more than just a form to type an article!
Wordpress is also simpler when you want to connect to a local editor like Live Writer. This may be done with Drupal, but it is much more challenging, as evidenced by the procedure of configuring Live Writer for Drupal.
Categories
Were the Wordpress user go the most in trouble when he moves to Drupal, is in category management. Wordpress is very simple, it has a list of categores and a new post is associated to one of them.
Drupal lets you create complex hierarchical taxonomies to classify items according to different points of view.
Statistics
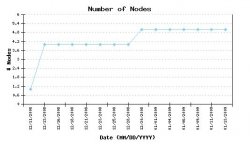
Many plugins statistics can complement Wordpress, while Drupal offers an integrated statistical tools complete with graphics (see right).
It is a rare case where Drupal offers in the core a tool that is external to Wordpress. This is perhaps because the statistical tool created by the developers of Wordpress works by storing data on the Wordpress' site, which is not necessarily the best choice for the webmaster.
Resources
Wordpress uses 10 SQL tables while Drupal requires 46, a number that is growing rapidly and reaches 68 when we added the modules that provide the basic features of Wordpress.
It is clear that the resource consumption of Drupal is much more important!
Extensions
Wordpress has a larger number of extensions that Drupal. Both CMS integrates basic functions that must be added as an option to the other.
Functions included in Drupal core, not in Wordpress.
- Pagination.
- Statistics.
Wordpress internal functions, to add in the form of plug-in to Drupal.
- Tag Cloud.
- Friendly URLs made of keywords.
- WYSIWYG editor.
Cron setting required
Drupal does not update automatically accessories to page hits such as sitemap, tag cloud ... We must configure the cron task on the server so that it does so at regular intervals.
Wordpress performs updates when articles are edited.
Another detail that shows Drupal is not a piece of software to free the webmaster of tasks of site management!