About Plugins in Chrome (deprecated)
Description of the command about: plugins in the Chrome browser and comparison of the list of add-ons of other browsers.
about:plugins
When you type this command in the address bar, the browser displays the list of modules added to the browser, which are most often available in the form of additional plugins.
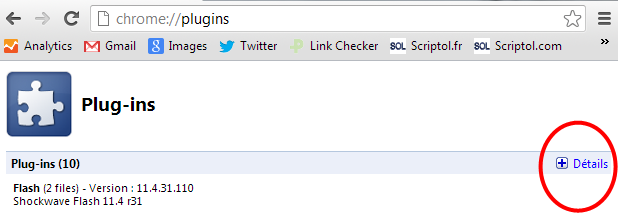
List of plugins in Chrome
For history, they are no longer in the browser.
- ActiveX plug-in.
- Google Gears.
- Google Gadget Plugin.
- Adobe Acrobat.
- Google Update.
- Google Updater.
- Shockwave Flash.
- Windows Presentation Foundation.
- Default Plug-in.
We can see by comparing with other browsers that Google does not include Java by default.
Details of plugins
Remoting Viewer
Work with the the Remote Desktop application (which control remotely your computer). Disable this plugin if you do not use this app.
Chrome PDF Viewer
Used to display PDF files with the browser.
Google Update
For updates to the browser.
Windows Presentation Foundation
A graphical interface system in .NET, which manages the processing of XAML.
Google Gadget (Option)
These gadgets are displayed on a Web page thanks to the plugin, or on the desktop.
Default Plug-in
Used to install additional plugins.
Comparison with Firefox
The same command in Firefox could displays the following list, according to what you have installed:
- Adobe Acrobat
- Google Gadget Plugin.
- Google Update.
- Java Platform.
- Windows Presentation Foundation.
- Zeon Plus. Displays PDF files.
They are almost the same modules, even if some could have been added to the browser. Additional Java support.
The differences are the ActiveX and Gears plugins which are not present in Firefox.
Comparison with Internet Explorer
The Microsoft's browser does not recognize the command but you can have the list from the browser:
- Go to Tools -> Internet Options.
- In History, click Settings.
- Click on View objects.
Not all plugins appear in the list.
Comparison with Safari
Although it shares technologies with Chrome, Safari does not support the command, but you get the list from the options.
- Click on Help.
- Click on Install modules.
This list is displayed:
- Google Gadget Plugin.
- Apple Java Plug-In.
- Shockwave Flash.
- Windows Presentation Foundation.
- Adobe Acrobat.
- Google Update.
- Silverlight Plug-In.
This is the same list as for Firefox.
Conclusion
The particularity of Chrome is the integration of Gears by default and ActiveX (which is also part of Internet Explorer). It is a browser that is ready for Web applications with plugins as it is in its design.
Obviously the list of add-ons will evolve with what the user will install in the future.