Internet Explorer 10 and HTML 5

With Internet Explorer 10, Microsoft wants to develop further support for HTML 5 and CSS 3 and allow to make immersive apps.
IE10 is available for Windows 7 in all countries since 26 February 2013.
HTML 5 native, CSS3 gradients, flexbox
To speed up the browser and provide access to Windows functions, Microsoft has removed all the intermediate layers between applications in IE 10, and the base system, providing direct access to the functions thereof.
A Web application works as a Windows application.
Critics say that the term is rather superficial, all the current browser using material acceleration having similar capacities.
Internet Explorer is also a component of Windows 8 for immersive applications.
New HTML 5 features supported:
- Drag and drop.
- File Reader API.
- Forms validation.
- IFrame support the sandbox attribute for a secure excution in a separate environment.
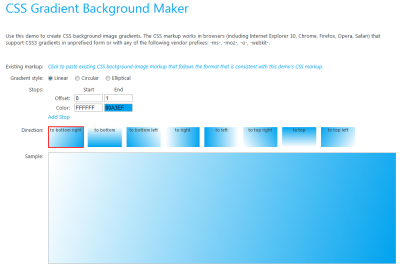
A tool to make gradients
In CSS, shadows are now supported to create widgets similar to the native components of mobile phone systems.
Microsoft actually provides for demonstration an online tool to illustrate this new gradient function.
3D transforms and transitions are added too.
Inspired by the Mozilla XUL interface language, flexbox is a tag for a flexible layout allowing dynamically display of content depending on the size of the screen, on the desktop or on a mobile device.
The float properry may be positionned inside the page now and not only at left or at right.
More improvements and changes:
- JavaScript 5, which adds the method JSON.parse and new properties to objects.
- async attribute, to run scripts asynchronously.
- Web Workers API to run script in the background without effect on the display.
- The feature "Do not track" is enabled by default, which will prevent the ads to fit the focus of the user.
- The Flash Player is not a plugin but is now part of the browser, and it allows for applications in the Metro style.